Automobile prices in market equilibrium present a fascinating interplay of economic forces, where supply and demand converge to establish a delicate balance. This article delves into the dynamics of this equilibrium, examining the factors that influence it and exploring the implications for both consumers and the industry.
The concept of market equilibrium in the automobile market is a fundamental principle that governs price formation. It occurs when the quantity of automobiles supplied by manufacturers matches the quantity demanded by consumers at a specific price. This equilibrium price is the result of a dynamic adjustment process that balances the forces of supply and demand.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
In a market economy, the prices of goods and services are determined by the interaction of supply and demand. Equilibrium occurs when the quantity of a good or service supplied equals the quantity demanded at a particular price. In the automobile market, this equilibrium price is the point where the supply curve and the demand curve intersect.
Factors Influencing Supply and Demand, Automobile prices in market equilibrium
- Consumer preferences: Changes in consumer tastes and preferences can shift the demand curve.
- Technological advancements: Innovations in technology can lead to increased production efficiency, shifting the supply curve.
- Government policies: Regulations and taxes can influence both supply and demand.
- Economic conditions: Factors such as income levels and interest rates can affect demand.
Market Equilibrium and Price Determination: Automobile Prices In Market Equilibrium
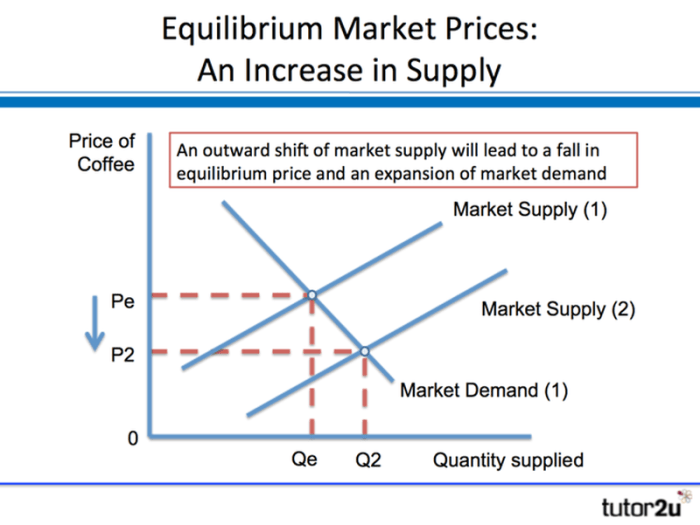
Equilibrium in the automobile market is established when the supply and demand curves intersect. At this point, the quantity of automobiles supplied equals the quantity demanded, and the market price is stable.
Price plays a crucial role in balancing supply and demand. If the price is too high, there will be an excess supply, and producers will be forced to lower prices to sell their inventory. Conversely, if the price is too low, there will be an excess demand, and consumers will be willing to pay a higher price to acquire the automobiles.
The equilibrium price can be illustrated using a supply and demand graph. The supply curve slopes upward, indicating that producers are willing to supply more automobiles at higher prices. The demand curve slopes downward, indicating that consumers are willing to demand fewer automobiles at higher prices.
Factors Affecting Equilibrium Prices
Equilibrium prices for automobiles are influenced by a range of economic and market factors.
- Consumer preferences: Changes in consumer preferences, such as a shift towards fuel-efficient vehicles, can lead to changes in demand and equilibrium prices.
- Technological advancements: Technological innovations, such as the development of electric vehicles, can lead to shifts in both supply and demand, impacting equilibrium prices.
- Government policies: Government regulations, such as fuel efficiency standards, can influence the supply of automobiles, leading to changes in equilibrium prices.
- Economic conditions: Economic factors, such as changes in interest rates or income levels, can affect demand and equilibrium prices.
Market Interventions and Equilibrium
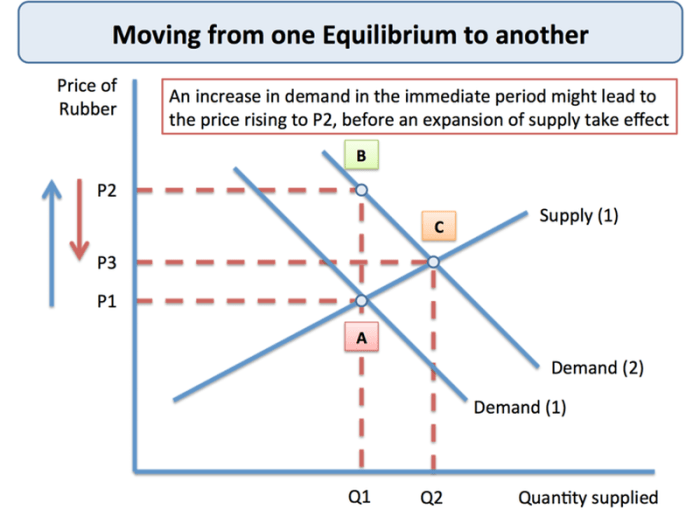
Government interventions, such as price controls or subsidies, can affect market equilibrium prices.
Price controls, such as price ceilings, can prevent prices from rising above a certain level. This can lead to a shortage of supply, as producers are less willing to produce automobiles at the lower price.
Subsidies, on the other hand, can lower the price of automobiles for consumers. This can lead to an increase in demand, as consumers are more likely to purchase automobiles at the lower price.
Long-Term Trends and Equilibrium Prices
Equilibrium prices for automobiles have exhibited long-term trends influenced by factors such as technological advancements, economic cycles, and societal changes.
Technological advancements have led to increased production efficiency and the development of new vehicle types, influencing both supply and demand and impacting equilibrium prices.
Economic cycles, such as recessions and periods of economic growth, can affect consumer demand and equilibrium prices.
Societal changes, such as urbanization and changes in lifestyle, can also influence demand and equilibrium prices.
Expert Answers
What is the significance of market equilibrium in the automobile market?
Market equilibrium ensures a balance between the quantity of automobiles supplied and demanded, leading to price stability and efficient resource allocation.
How do changes in consumer preferences affect equilibrium prices?
Shifts in consumer preferences can lead to changes in demand, which in turn can cause equilibrium prices to adjust to reflect the new market conditions.
What role does government intervention play in market equilibrium?
Government interventions, such as price controls or subsidies, can influence the supply or demand curves, thereby shifting the equilibrium price.