Unveiling the history of the atom worksheet PDF answers, this comprehensive guide embarks on an enlightening journey into the fascinating world of atomic science. From the fundamental building blocks of matter to the evolution of our understanding of the atom, this exploration delves into the discoveries and contributions of renowned scientists, shaping our comprehension of the microscopic realm.
As we delve into the intricacies of atomic structure, properties, and reactions, this guide provides a clear and engaging narrative, making complex concepts accessible and captivating. Prepare to unravel the secrets of the atom, its profound impact on our understanding of the universe, and its applications that shape modern technology and scientific advancements.
1. Definition of an Atom
An atom is the fundamental unit of matter, consisting of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, while the electrons orbit the nucleus at high speeds.
Basic Structure and Components
Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles:
- Protons:Positively charged particles located in the nucleus.
- Neutrons:Neutral particles located in the nucleus.
- Electrons:Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in electron shells.
The number of protons and electrons in an atom is equal, giving it a neutral overall charge.
2. History of the Atomic Model: History Of The Atom Worksheet Pdf Answers
The concept of the atom has evolved over centuries, with significant contributions from various scientists.
Key Scientists and Their Contributions
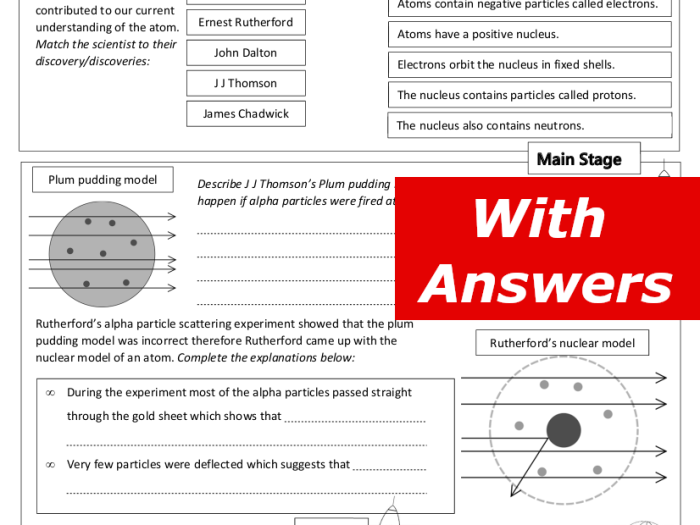
- Dalton (1803):Proposed the first atomic theory, stating that matter is composed of indivisible atoms.
- Rutherford (1911):Discovered the atomic nucleus and proposed the Rutherford model, which depicted the atom as a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
- Bohr (1913):Proposed the Bohr model, which introduced the concept of electron shells and explained the quantization of energy levels.
- Schrödinger (1926):Developed the quantum mechanical model, which describes the behavior of electrons as waves and predicts their probability distribution around the nucleus.
Timeline of Discoveries, History of the atom worksheet pdf answers
- 1803:Dalton’s atomic theory
- 1897:Discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson
- 1911:Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus
- 1913:Bohr’s model of the atom
- 1926:Schrödinger’s quantum mechanical model
3. Properties of Atoms
Atoms have various properties that determine their chemical and physical behavior.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus, which determines the element’s identity. The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
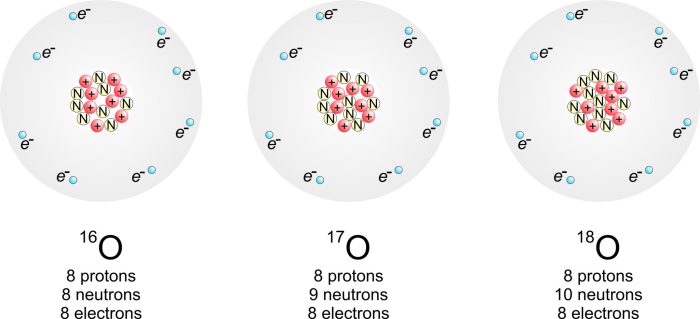
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons, resulting in isotopes. Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Periodic Table
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic numbers. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties due to their identical electron configurations.
4. Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear reactions involve changes in the atomic nuclei, releasing or absorbing energy.
Types of Nuclear Reactions
- Nuclear Fission:Splitting a heavy nucleus into smaller nuclei, releasing large amounts of energy.
- Nuclear Fusion:Combining two light nuclei into a heavier nucleus, also releasing energy.
- Radioactive Decay:Spontaneous disintegration of an unstable nucleus, releasing particles and energy.
Applications
- Energy Production:Nuclear power plants use fission to generate electricity.
- Medical Imaging:Radioisotopes are used in diagnostic imaging and cancer treatment.
- Scientific Research:Nuclear reactions are used to study the properties of atoms and subatomic particles.
Safety Considerations
Nuclear reactions can release harmful radiation, so proper safety measures must be implemented to prevent exposure and environmental contamination.
5. Atomic Spectroscopy
Atomic spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of light with atoms, providing insights into their structure and composition.
Principles
When atoms absorb or emit light, they do so at specific frequencies that correspond to energy transitions between electron shells.
Types of Atomic Spectra
- Emission Spectra:Light emitted by excited atoms, displaying bright lines at characteristic wavelengths.
- Absorption Spectra:Light absorbed by atoms, resulting in dark lines at specific wavelengths.
Applications
- Astronomy:Identifying elements in stars and galaxies based on their emission and absorption spectra.
- Materials Science:Characterizing the composition and structure of materials.
- Chemical Analysis:Identifying and quantifying elements in various samples.
FAQ
What is the significance of the history of the atom?
Understanding the history of the atom provides insights into the evolution of scientific thought and the development of our comprehension of the fundamental building blocks of matter.
How does the history of the atom relate to modern science?
The discoveries and advancements in atomic science have laid the foundation for modern fields such as nuclear physics, quantum mechanics, and materials science, shaping our technological advancements and scientific understanding.
What are the key applications of atomic science?
Atomic science has led to practical applications in diverse fields, including energy production, medical imaging, and materials engineering, transforming our daily lives and shaping the future of technology.