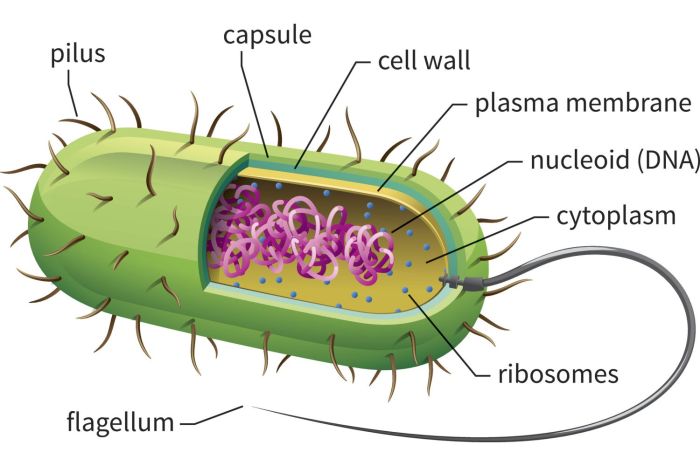
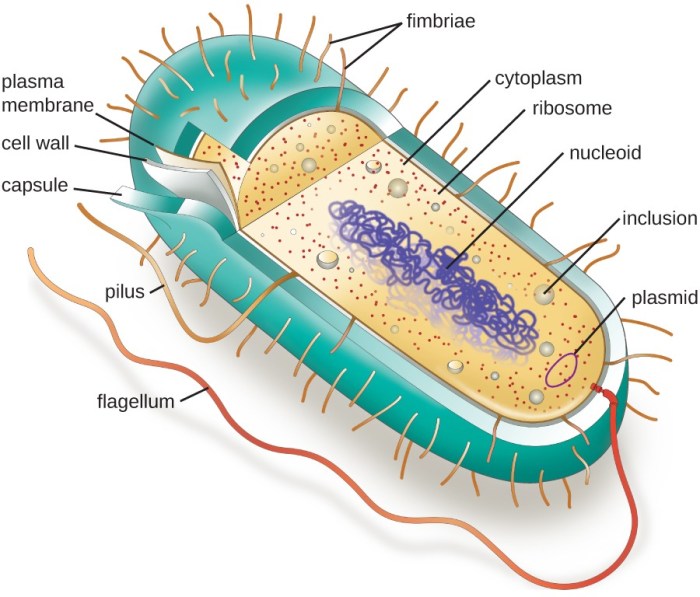
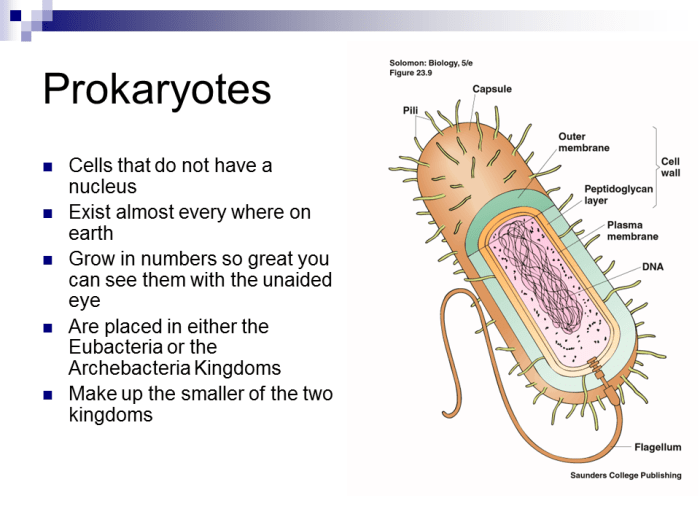
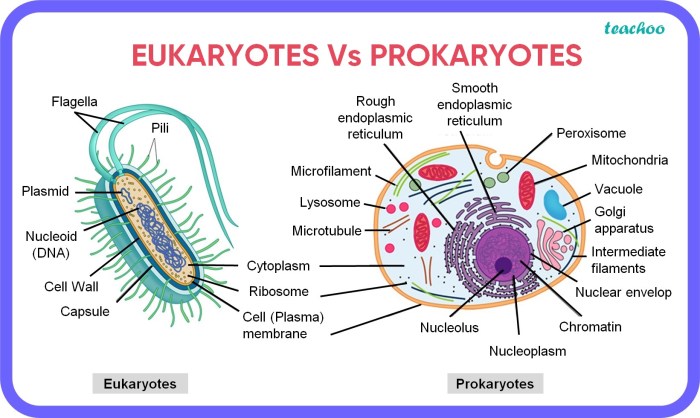
Which statement is true regarding bacteria? Bacteria are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They exhibit diverse shapes, including cocci, bacilli, and spirilla, and some possess flagella and pili for motility and attachment.
Bacteria are classified into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups based on their cell wall structure, with staining techniques aiding in their identification. Medically significant bacteria belong to both groups, causing a wide range of infections.
Characteristics of Bacteria
Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms, meaning they lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They are typically unicellular, but some species can form multicellular structures. Bacterial cells have a simple structure consisting of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a single circular chromosome.
Bacterial Shapes
- Cocci: Spherical
- Bacilli: Rod-shaped
- Spirilla: Spiral-shaped
Flagella and Pili
Some bacteria possess flagella, whip-like structures used for motility, and pili, hair-like structures used for attachment to surfaces.
Classification of Bacteria
Bacteria are classified into two main groups based on their cell wall structure: Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
- Thick cell wall with multiple layers of peptidoglycan
- Retain crystal violet dye during Gram staining
- Examples: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae
Gram-Negative Bacteria
- Thin cell wall with a single layer of peptidoglycan
- Do not retain crystal violet dye during Gram staining
- Examples: Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bacterial Metabolism
Bacteria exhibit diverse metabolic pathways, allowing them to utilize various substrates for energy production.
Aerobic Respiration
- Use oxygen as the final electron acceptor
- Produces large amounts of ATP
- Examples: Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Anaerobic Respiration
- Use alternative electron acceptors, such as nitrate or sulfate
- Produces less ATP than aerobic respiration
- Examples: Clostridium perfringens, Desulfovibrio desulfuricans
Fermentation
- Break down glucose without using an electron transport chain
- Produces small amounts of ATP
- Examples: Lactobacillus acidophilus, Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Bacterial Pathogenesis
Bacteria can cause disease through various mechanisms, including the production of toxins, invasion of host cells, and disruption of host defenses.
Mechanisms of Pathogenesis
- Toxins: Harmful substances that damage host cells or tissues
- Invasion: Entry into host cells or tissues, leading to damage or replication
- Disruption of host defenses: Interference with immune responses or cell function
Examples of Bacterial Pathogens
- Salmonella enterica: Causes salmonellosis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Causes tuberculosis
- Chlamydia trachomatis: Causes chlamydia
Antibacterial Agents: Which Statement Is True Regarding Bacteria
Antibacterial agents are substances that inhibit the growth or kill bacteria. They are used to treat bacterial infections.
Mechanisms of Action
- Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
- Interference with protein synthesis
- Disruption of DNA replication
Examples of Antibacterial Agents, Which statement is true regarding bacteria
- Penicillin: Inhibits cell wall synthesis
- Tetracycline: Inhibits protein synthesis
- Ciprofloxacin: Inhibits DNA replication
Antibiotic Resistance
Bacteria can develop resistance to antibacterial agents, making treatment difficult or impossible. This is a major public health concern.
Applications of Bacteria
Bacteria play beneficial roles in various fields, including biotechnology, medicine, and industry.
Biotechnology
- Production of antibiotics and enzymes
- Genetic engineering and cloning
- Bioremediation
Medicine
- Probiotics: Live bacteria that promote health
- Diagnostics: Detection of pathogens and diseases
- Development of new vaccines and therapies
Industry
- Production of biofuels
- Waste management and wastewater treatment
- Food processing and preservation
FAQ Explained
What is the unique characteristic of bacterial cells?
Bacterial cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
How are bacteria classified based on their cell wall structure?
Bacteria are classified into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups based on their cell wall structure.
What is the role of flagella and pili in bacteria?
Flagella and pili aid in bacterial motility and attachment, respectively.
How do bacteria cause disease?
Bacteria can cause disease through various mechanisms, including the production of toxins and the invasion of host cells.
What are the different types of antibacterial agents?
Antibacterial agents include antibiotics, disinfectants, and antiseptics, which target different mechanisms to combat bacterial infections.