Parties primaries caucuses and conventions teacher guide – Parties, Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions: A Comprehensive Guide for Teachers introduces a journey through the captivating landscape of electoral processes, providing an in-depth understanding of the mechanisms that shape political landscapes and influence candidate selection.
This guide delves into the intricacies of each component, exploring their purpose and role within the electoral system, empowering educators with the knowledge to effectively navigate and convey these concepts to their students.
Overview of Parties, Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions
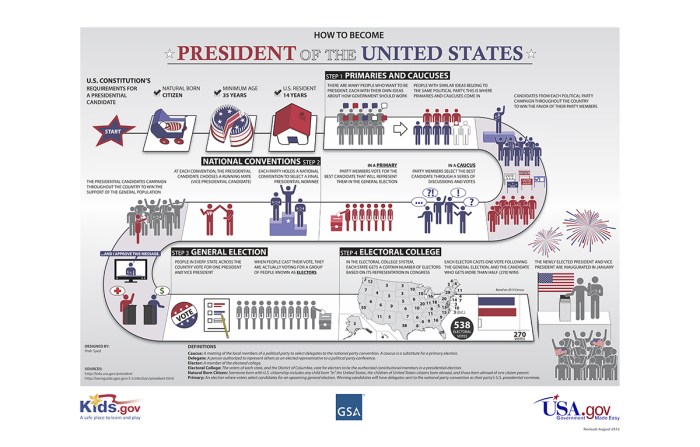
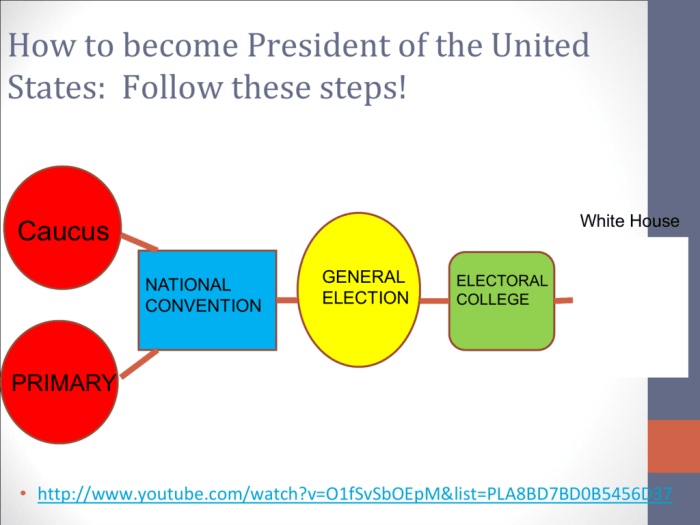
The electoral process in the United States involves a complex system of political parties, primaries, caucuses, and conventions. Each of these components plays a crucial role in selecting candidates for public office and shaping the political landscape.
Political parties are organizations that promote specific ideologies and agendas. They endorse candidates for office and mobilize voters to support them. Primaries and caucuses are elections held by political parties to select their nominees for office. Conventions are gatherings of party delegates who formally nominate candidates and adopt party platforms.
Types of Primaries and Caucuses
Primaries
- Closed Primary:Only registered members of a particular party can vote in the primary.
- Open Primary:Voters can choose to vote in the primary of any party, regardless of their party affiliation.
- Blanket Primary:Voters can vote for candidates from any party on the same ballot.
Caucuses, Parties primaries caucuses and conventions teacher guide
- Traditional Caucus:Party members gather in local meetings to discuss and vote on candidates.
- Hybrid Caucus:A combination of traditional caucuses and mail-in or online voting.
The Role of Delegates in Conventions
Delegates to national party conventions are selected through primaries and caucuses. They represent the views of their constituents and participate in the nomination process. The number of delegates each state receives is based on factors such as population and past election results.
At the convention, delegates cast their votes for the party’s presidential and vice-presidential nominees. The candidate who receives the majority of delegate votes becomes the party’s nominee.
The Convention Process

- Pre-Convention Activities:Delegates are selected through primaries and caucuses.
- Convention:Delegates gather to nominate candidates, adopt the party platform, and conduct other party business.
- Post-Convention Activities:The party’s nominees campaign for the general election.
The Impact of Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions

Primaries, caucuses, and conventions play a significant role in the electoral process by:
- Allowing voters to participate in the selection of candidates.
- Narrowing down the field of candidates and building consensus.
- Uniting the party behind its nominees.
- Influencing the tone and direction of the general election.
Examples of Historical Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions: Parties Primaries Caucuses And Conventions Teacher Guide
Significant primaries, caucuses, and conventions in U.S. history include:
- 1860 Republican National Convention:The nomination of Abraham Lincoln, which led to the outbreak of the Civil War.
- 1968 Democratic National Convention:The nomination of Hubert Humphrey amid protests and violence.
- 2008 Democratic National Convention:The nomination of Barack Obama, the first African American presidential nominee of a major party.
Controversies and Challenges
Primaries, caucuses, and conventions have faced controversies and challenges, including:
- Access to the Ballot:Concerns about whether all candidates have equal opportunities to participate in primaries and caucuses.
- Voter Suppression:Efforts to restrict voter participation, particularly among marginalized groups.
- Convention Rules:Disputes over the rules governing delegate selection and candidate nomination.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of a primary?
Primaries allow voters to express their preference for a party’s nominee in an election.
How do caucuses differ from primaries?
Caucuses are gatherings of voters who meet to discuss and vote on their preferred candidates, while primaries are elections conducted by secret ballot.
What is the role of delegates in conventions?
Delegates are individuals chosen to represent their state or district at a political convention, where they vote to nominate the party’s presidential candidate.